Introduction
In an era where sustainability is becoming integral to business strategies, investing in solar panels presents a compelling opportunity for companies aiming to reduce their carbon footprint while also cutting energy costs. As energy prices fluctuate and environmental regulations tighten, solar energy offers both financial and ecological advantages. This guide will explore the various aspects of investing in solar panels, from understanding the technology to evaluating the financial implications and implementing the system.
Understanding Solar Technology
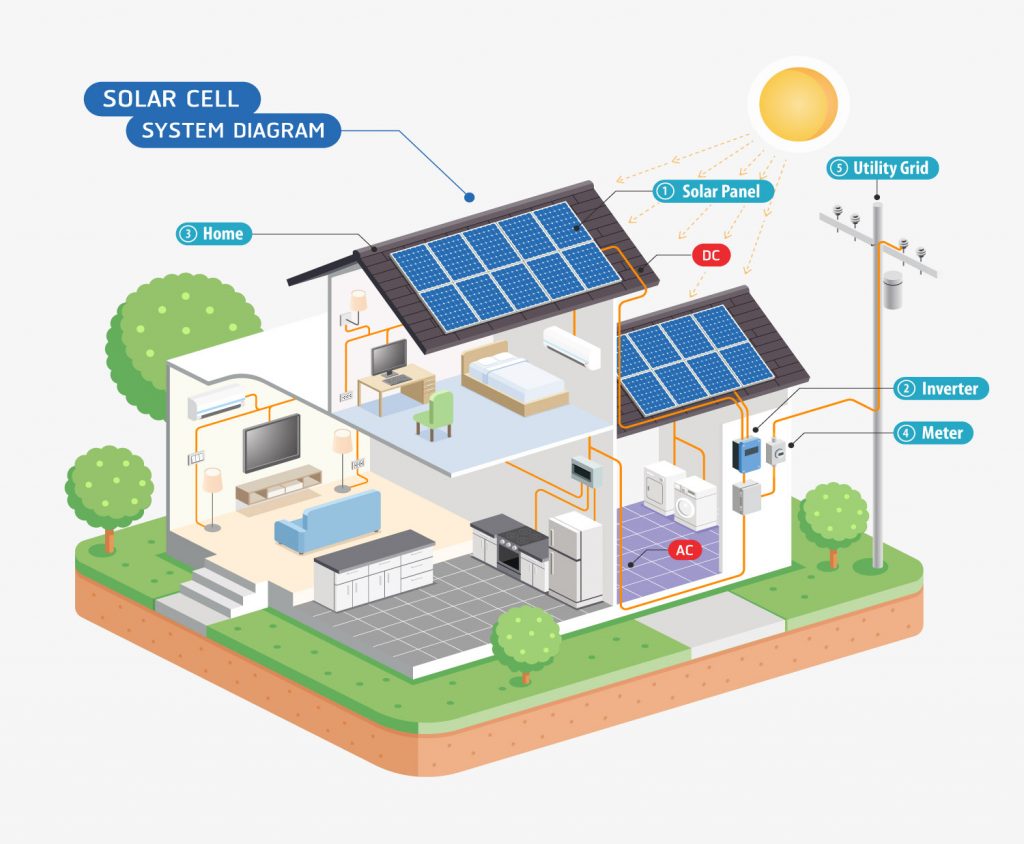
Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) panels, convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are typically composed of silicon cells which absorb sunlight and create an electric field. There are various types of solar panels available, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the differences can help businesses choose the right type of panel based on their specific needs.
Types of Solar Panels
- Monocrystalline Panels: Known for their high efficiency and longevity, these panels are made from a single crystal structure. They generally perform better in low-light conditions and have a sleek appearance.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Constructed from multiple silicon crystals, these panels are generally less efficient than monocrystalline options but are often more affordable. They can be an excellent choice for budget-conscious businesses.
- Thin-Film Panels: These lightweight panels are created by depositing a thin layer of photovoltaic material onto a surface. While they are less efficient per square foot than crystalline panels, they are more versatile and can be installed in various locations, including on curved surfaces.
Assessing Your Energy Needs
Before investing in solar panels, businesses must assess their energy consumption patterns. Conducting an energy audit will help identify current electricity usage and peak consumption times, which are crucial for determining the size and capacity of the solar installation needed. Understanding these factors allows for better alignment of solar output with the business’s energy demand.
Financial Considerations
Investing in solar panels requires an upfront capital investment but can lead to significant long-term savings. Here are critical financial aspects to consider:
Initial Investment and Incentives
The cost of solar panels can vary based on the type, size, and installation complexity. However, several incentives exist that can offset initial costs:
- Federal Tax Credits: In the U.S., businesses can benefit from the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), allowing them to deduct a significant percentage of the installation costs from their federal taxes.
- State Incentives: Many states offer additional financial incentives, such as rebates or tax exemptions, making solar energy more economically viable.
Long-Term Savings
Once operational, solar panels can drastically reduce electricity bills. The extent of savings will depend on the amount of sunlight the location receives, the size of the solar system, and energy usage patterns. Additionally, solar energy often provides economic protection against rising energy prices.
Financing Options
Businesses have several financing options available, including:
- Purchasing: Buying solar panels outright provides the highest savings in the long run but requires a large initial investment.
- Leasing: Operating leases allow businesses to use solar panels without a significant upfront cost. While this option may lead to lower overall savings, it provides immediate benefits and cash-flow neutrality.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): In this arrangement, a third party owns the solar system and sells the energy produced back to the business at a set rate, often lower than the typical utility rates.
Choosing a Solar Installer

Selecting a reputable solar installer is vital to ensure quality service and system performance. Businesses should conduct thorough research, seeking installers with strong credentials, positive customer reviews, and experience with installations similar to their project.
Key Factors in Choosing an Installer
- Certifications: Look for installers with certifications from the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) or similar organisations.
- Experience: Choose installers with proven experience in the local market and familiarity with the specific regulations and incentives available.
- References: Asking for references and reviewing past projects can provide insights into an installer’s quality of work and customer satisfaction.
Installation Process
The installation of solar panels typically follows a structured process:
- Site Assessment: The installer examines the proposed location for solar panel installation, considering shading, roof orientation, and structural integrity.
- Design: A custom solar system design is created, taking into account the unique energy needs of the business.
- Permitting: Necessary permits and approvals are obtained from local authorities.
- Installation: The solar system is installed according to the agreed-upon design and safety standards.
- Inspection: Following installation, the system undergoes inspection to ensure it meets regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Monitoring
While solar panels require minimal maintenance, regular inspections and performance monitoring are essential for optimal efficiency. Businesses should establish a maintenance schedule and consider implementing monitoring systems to track energy production and system performance in real-time.
Regular Maintenance Activities
- Cleaning: Removing debris, dust, and snow can improve the efficiency of solar panels. Regular cleaning schedules may be needed, especially in dusty environments or locations with significant snowfall.
- Inspections: Routine inspections can help spot issues with system performance, electrical connections, and inverter functionality before they become major problems.
Environmental Impact
The decision to invest in solar panels can significantly contribute to reducing a business’s carbon footprint. Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that helps decrease reliance on fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to solar energy, businesses not only comply with increasing sustainability regulations but also align with the growing expectations of environmentally conscious consumers.
Conclusion
Investing in solar panels is a strategic decision for businesses aiming to enhance energy independence, reduce operational costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability. By understanding solar technology, assessing energy needs, navigating financial considerations, choosing reputable installers, and implementing effective maintenance strategies, businesses can maximise the benefits of their solar investment, positioning themselves as forward-thinking leaders in their industries. As the shift towards renewable energy intensifies, solar panels will play a critical role in the sustainable future of businesses worldwide.

